Your thyroid gland performs various functions ranging from metabolism to brain development. Every cell in your body requires thyroid hormones to perform their assigned work. The thyroid gland produces two hormones:
- 90%- thyroxine (T4)
- 10% - triiodothyronine (T3)
An underactive thyroid means that your thyroid is not secreting enough hormones. This might lead to symptoms of hypothyroidism. If your thyroid is overactive and secretes excess hormones, it causes hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid function tests (TFTs) help to measure the level of hormones. They also help assess the functioning of the thyroid gland.
In this blog, we will understand what TFTs measure and how to interpret the results.
Read on to know more.
What are thyroid function tests (TFTs)?
A TFT is a series of blood tests carried out to detect or monitor various thyroid disorders. The tests included are:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone test (TSH test)
- Thyroxine test (T4 test)
- Triiodothyronine test (T3 test)
Additionally, your doctor may also advise testing for thyroid antibodies.
Doctors generally recommend a TFT if you are experiencing symptoms of thyroid disease. As there are various causes of thyroid problems, TFT can narrow down the diagnosis in each case.
The problem can lie in the gland itself or in the pituitary gland that stimulates the production of thyroid hormones. TFT can help localize the disease.
TSH Test:
The TSH test is the most common test performed to identify thyroid diseases. Many people misunderstand TSH to be the hormone produced by the thyroid gland. But TSH is a hormone secreted and released by the pituitary gland in the brain.
This hormone stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4 hormones. In simple words, TSH makes sure that thyroid hormones are released into blood circulation as required. To do this, it monitors the level of thyroid hormone and stimulates the gland accordingly.
TSH is often advised as an initial test before starting thyroid treatment. When patients experience symptoms of thyroid disease, it is usually the first test performed.
The normal range of TSH is 0.5 - 4.0 mIu/L in adults.
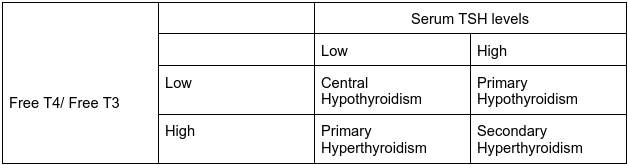
When the level is higher, it means TSH is stimulating the thyroid more to produce T4 hormones. Levels above 4.5 mIU/L may indicate hypothyroidism
When the level is lower than normal, it means that T3 and T4 levels may be high. Due to this, the body is trying to reduce the stimulation of the thyroid gland. Levels below 3.5 mIU/L may indicate hyperthyroidism.
However, TSH levels alone are not enough. To interpret the results correctly, more tests are needed.
T4 Test:
T4 or thyroxine is the major hormone produced by the thyroid gland. There are two forms of T4 present in the body:
- Bound T4
- Free T4
Bound T4 is attached to proteins and cannot be utilized by the body. Free T4 is the one that actually performs metabolic functions in the body.
More than 95% of T4 in the body is in the bound state. Only 5% is available for the organs and tissues to use as free T4.
A total T4 test measures both free T4 and bound T4. But a free T4 test measures only the amount of free T4 in the blood.
Normal levels:
In adults, the normal level of total T4 ranges from 5-12(mcg/dl) of blood. And the normal level of free T4 ranges from 0.8-1.8 (ng/dl) of blood. Anything below or above the range indicates a thyroid problem.
High TSH levels with low free T4 and total T4 are usually seen in hypothyroidism.
T3 Tests:
T3 or triiodothyronine hormone is only about 10% of the hormones produced by the thyroid gland. T3 is the active form of the hormone needed in the body. Hence, even T4 is converted to T3 to perform its functions.
Similar to T4, there are two forms of T3 available in the body.
- Bound T3
- Free T3
Bound T3 is attached to transport proteins, whereas free T3 is free and can be used by the cells.
The normal level of total T3 ranges from 75-195 ng/dl. The normal level of free T3 ranges from 0.2-0.5ng/dl.
If the TSH level is low, and total T3 and free T3 are high, then a person might be suffering from hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid antibodies tests:
Antibodies protect us from foreign invaders and fight against various diseases. Autoimmunity is when your antibodies recognise your own cells as foreign and attack them. When the thyroid antibodies react against thyroid cells, it results in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Grave's disease.
Thyroid antibody tests detect if the disease is because of autoimmunity. This is the most common cause of thyroid disease. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a form of autoimmune hypothyroidism. Antibodies can also cause hyperthyroidism, known as Grave's disease.
There are three major types of thyroid antibodies present in our body:
- Anti-thyroid peroxidase (TPO)
- TSH receptor antibodies
- Anti thyroglobulin (TG)
Anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO):
The TPO enzyme aids the thyroid gland in producing both T4 and T3. But when thyroid antibodies attack TPO, the production gets affected. This results in the development of Hashimoto’s autoimmune thyroiditis in the body.
The normal level of TPO antibodies is less than 9 IU/mL. When TPO results are negative, it means there is no autoimmune disorder. If the test results are positive, you might suffer from Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
It is important to note that the presence of the antibodies does not necessarily mean that you have thyroid disease. However, you could be at a higher risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease in the future.
Thyroglobulin (TgAb):
Thyroglobulin is the main precursor from which all thyroid hormones are formed. Antibodies against it affect the production of T3 and T4 directly. This results in hypothyroidism.
Anti - TG antibodies' typical values are less than 4 IU/mL. If the test results are more than 4 IU/mL, it could indicate Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
TSH receptor antibodies:
TSH begins to work by binding to structures called TSH receptors on the thyroid gland. TSH receptor antibodies mimic TSH. They stimulate the thyroid gland to constantly produce more hormones.
This in turn forces the thyroid gland to release more T3 and T4 hormones into blood circulation. As a result, hyperthyroidism develops in an individual’s body.
Normal values of TSH receptor antibodies are less than 1.75 IU/L. The person might be suffering from Grave’s disease (autoimmune hyperthyroidism) if the values are abnormal.
Factors affecting thyroid test results:
Thyroid function tests are performed to understand how well your thyroid is working. If the results are abnormal, then the person might suffer from any thyroid disorders. Certain external factors can also affect your test results. These include
- Illness
- Medication
- Pregnancy
- Lifestyle
These factors might result in improper results and a wrong interpretation. Visit a trained thyroid specialist to make sure that your test results are interpreted correctly.
Final words:
Identifying the cause is the first step in the treatment of thyroid disease. TSH test, T4, T3, and thyroid antibodies test help find the cause of thyroid disease. A comprehensive test panel also helps in monitoring the response to treatment
Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Grave's disease are autoimmune conditions that commonly cause thyroid disease. Diagnosing them early is important and can have a huge impact on the treatment plan.
If you want to learn more about the management of these problems, we can help you. Join the Jeevam Health family to begin your root cause treatment.

